EMPOWERMENT THROUGH KNOWLEDGE: CONQUERING LOW BACK PAIN
Low back pain is a common and often debilitating condition that can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. Whether it’s a dull, nagging ache or a sharp, intense pain, low back pain can significantly impact your quality of life. In this blog post, we will explore the various aspects of low back pain, from its causes and symptoms to prevention and treatment options. Whether you’re currently suffering from low back pain or simply interested in learning more about it, this comprehensive guide aims to provide you with the knowledge and insights you need.
WHAT IS LOW BACK PAIN?

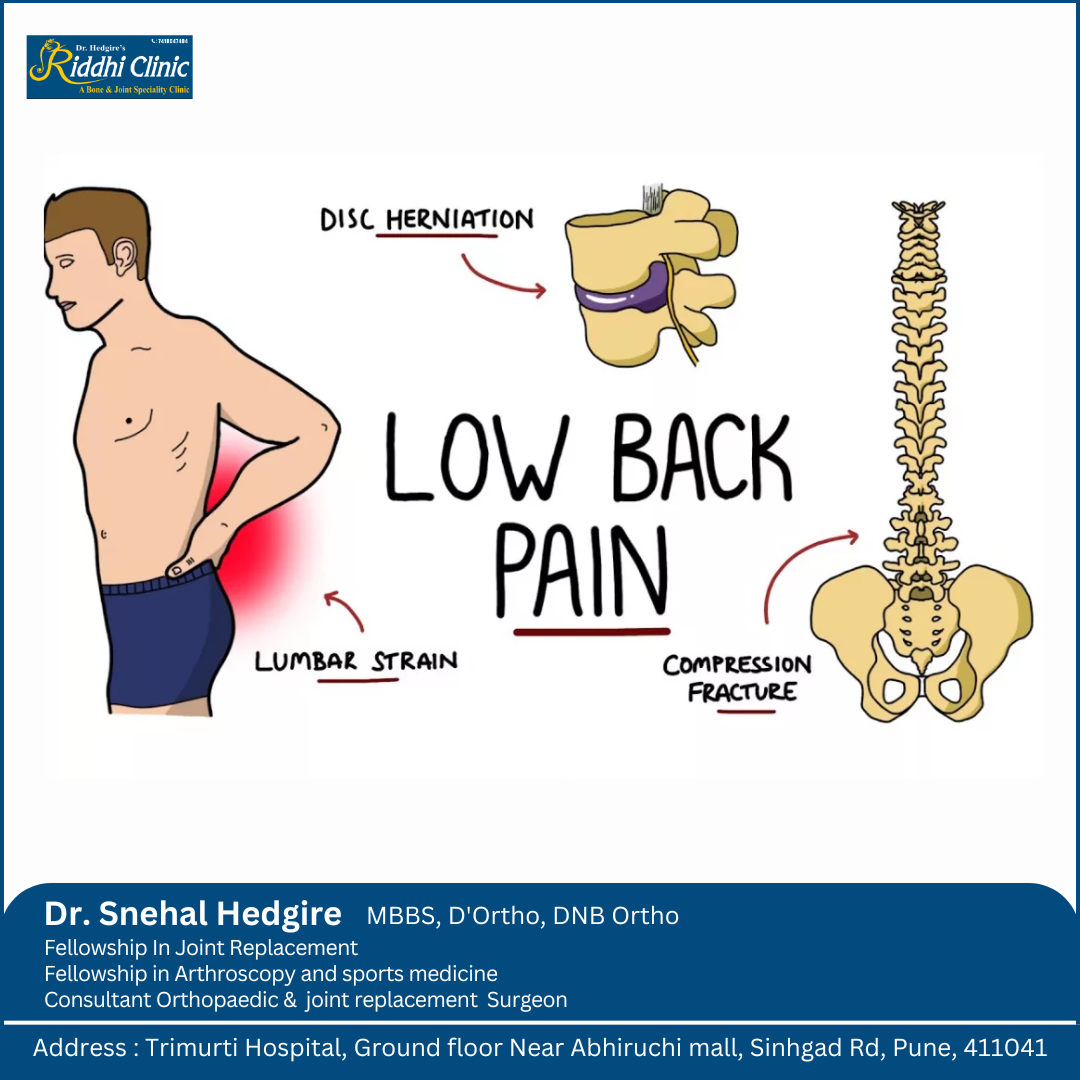
Low back pain, often abbreviated as LBP, refers to discomfort, pain, or soreness in the lower part of the back, specifically the lumbar region. It is one of the most prevalent musculoskeletal disorders globally, affecting people of all ages. Low back pain can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-lasting), and its severity can range from mild to severe.
TYPES OF LOW BACK PAIN

Low back pain can manifest in various forms and be categorized based on its characteristics and underlying causes. Understanding the types of low back pain is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Here are some common types:
- Mechanical Low Back Pain:
- Acute Mechanical Low Back Pain: This type of pain is typically caused by sudden trauma or strain, such as lifting a heavy object improperly or overexertion during physical activity. It is usually short-lived and may resolve with rest and self-care.
- Chronic Mechanical Low Back Pain: Chronic mechanical low back pain results from ongoing wear and tear on the spine or muscles. It can be associated with muscle imbalances, poor posture, or repeated microtrauma. This type of pain lasts for 12 weeks or longer.
- Radicular Pain (Sciatica): Radicular pain occurs when a spinal nerve root is compressed, leading to pain that radiates along the nerve’s path.
- Referred Pain: Referred pain is discomfort that is felt in the lower back but originates from a different location, such as the internal organs. For example, kidney stones or infections may cause referred pain in the lower back.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: This condition is not a disease but rather a natural part of aging. Over time, the intervertebral discs that cushion the spine can lose their elasticity and become less effective at absorbing shock. This can lead to chronic, dull low back pain.
- Spinal Stenosis: Spinal stenosis is a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal. This can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, causing pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower back and legs.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Ankylosing spondylitis is a form of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing stiffness and pain. It typically begins in the sacroiliac joints (located at the base of the spine) and can lead to chronic low back pain.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain and tenderness in the muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Low back pain is a common symptom for individuals with fibromyalgia.
- Spondylolisthesis: This condition occurs when one vertebra slips forward over the one below it. It can cause lower back pain and may also lead to nerve compression.
- Piriformis Syndrome: The piriformis is a small muscle in the buttocks. When it becomes tight or spasms, it can compress the sciatic nerve and result in symptoms similar to sciatica.
- Muscle Imbalance or Weakness: Imbalances in the muscles supporting the spine, including the core muscles, can lead to low back pain. These imbalances can result from poor posture, sedentary lifestyles, or previous injuries.










